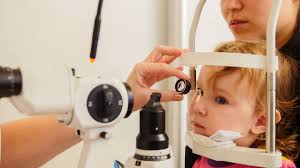
Children’s eye health plays a vital role in their overall growth, learning ability, and social development. Vision problems during childhood can affect reading skills, coordination, and classroom performance if left undiagnosed. Many eye conditions begin subtly, making regular eye assessments essential. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment can prevent long-term visual difficulties and support healthy eye development throughout childhood.
A paediatric ophthalmologist in Mumbai is trained to assess eye conditions in children of all ages, from infants to adolescents. These specialists understand how visual problems affect a child’s development and can recommend suitable treatment options based on the child’s age, condition, and visual needs. Early medical guidance ensures that both non-surgical and surgical treatments are used effectively and safely.
Common Paediatric Eye Conditions Requiring Treatment
Several eye conditions commonly affect children and may require timely treatment to support normal vision. Understanding these conditions helps parents recognise early warning signs and seek professional care when needed.
- Refractive Errors: Conditions such as myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism cause blurred vision and difficulty focusing. These issues are usually managed with prescription glasses or contact lenses. Early correction helps children participate confidently in academic and recreational activities.
- Strabismus: Commonly known as squint, strabismus occurs when the eyes do not align properly. It may interfere with depth perception and visual coordination. Treatment often begins with glasses or eye exercises, with surgery considered if alignment does not improve.
- Amblyopia: Also called lazy eye, amblyopia develops when one eye becomes weaker due to poor visual stimulation. Non-surgical treatments, including patching or atropine therapy, are most effective when started early. Surgical treatment may be required if an underlying structural problem exists.
- Congenital Cataracts: Some children are born with cataracts that cloud the eye’s natural lens. Surgical removal is often necessary to restore vision, followed by corrective lenses to support visual development. Early treatment is essential to avoid permanent vision loss.
- Childhood Glaucoma: This rare condition causes increased pressure inside the eye, which may damage the optic nerve. Management may begin with medication, but surgery is often required to protect vision and prevent further damage.
Early identification and appropriate treatment of these conditions significantly improve visual outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Paediatric Eye Conditions
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of management for paediatric eye conditions. These approaches aim to correct vision or manage symptoms without invasive procedures.
Common non-surgical treatments include:
- Prescription Glasses or Contact Lenses: Correct refractive errors and improve visual clarity.
- Patching Therapy: Encourages the weaker eye to develop strength in cases of amblyopia.
- Eye Exercises: Help improve eye coordination and alignment, particularly in mild strabismus.
- Medication: Eye drops or ointments may be prescribed for infections, inflammation, or glaucoma pressure control.
These treatments are suitable for children and are reviewed regularly to support visual development. Regular follow-up visits ensure that the chosen method continues to meet the child’s visual needs.
Surgical Treatments for Paediatric Eye Conditions
Surgical treatment is recommended when non-surgical methods are insufficient or the condition is severe. The goal of surgery is to correct structural problems and support long-term visual function.
Common surgical procedures include:
- Strabismus Surgery: Adjusts eye muscles to improve alignment and binocular vision.
- Cataract Removal: Removes the cloudy lens and supports vision restoration with corrective lenses.
- Glaucoma Surgery: Helps regulate eye pressure and protect the optic nerve.
- Corrective Surgery for Structural Abnormalities: Addresses congenital defects affecting eye function.
Paediatric eye surgery is performed with careful planning and monitoring. Post-operative care plays a crucial role in recovery and long-term success.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Follow-Up Care
Early diagnosis is one of the most important factors in successful paediatric eye treatment. Children’s eyes continue to develop during the early years, making timely intervention essential. Regular follow-up appointments allow specialists to monitor progress, adjust treatments, and identify new concerns as the child grows. Consistent care ensures that vision improves steadily and complications are avoided.
When to Consult a Paediatric Ophthalmologist?
Parents should seek medical advice if a child shows signs such as squinting, frequent eye rubbing, difficulty focusing, blurred vision, or poor coordination. Early consultation with a paediatric ophthalmologist in Mumbai allows for thorough evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and a personalised treatment plan. Professional guidance ensures that children receive the most suitable care at every stage of visual development.
Conclusion
Paediatric eye conditions can be effectively managed through a combination of surgical and non-surgical treatments when addressed early. Conditions such as refractive errors, strabismus, amblyopia, congenital cataracts, and childhood glaucoma require careful assessment and ongoing care. With timely diagnosis, regular monitoring, and expert treatment, children can achieve healthy vision and improved quality of life.